Why anxiety is an electrical illness

A myth isn’t a lie - but a story that tells itself.
The history of anxiety was first told by its victors - psychiatrists who conjured a human history of suffering on notepads that have now become the Western medical model. This is how our collective story of anxiety now tells itself:
Anxiety is all in your head.
Women are hysterical.
Women have weak nerves.
At least that’s what the Titans of the Electrical Age, including Sigmund Freud made many believe.
People actually had and still have neurasthenia, meaning “weak nerves.” You’ve probably never heard of this mystery illness. Before you chalk it up to the land of make-believe, we’d like to take you down a dark alley that’s sure to sparkle your curiosity. Let’s take a stroll down Electric Memory Lane, where serene streets are no longer sacred, and tranquil nights are profane.
Women with hysteria under the effects of hypnosis, 1876–1880:
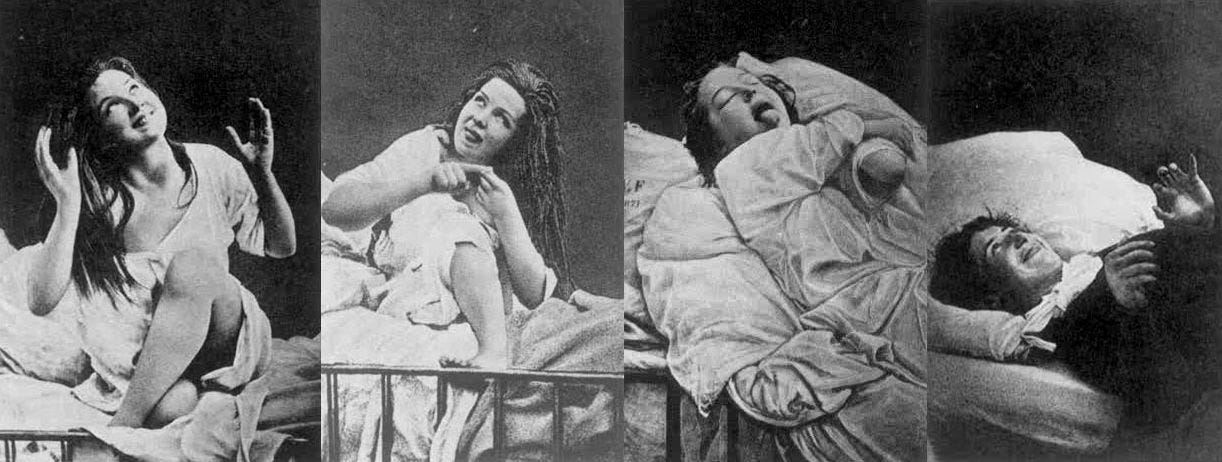
How women become hysterical
In the early 1800s, hysteria described a neurological condition of the body, not the mind. The “hystera” is Greek for uterus, and hysteria was a neurological disease that was believed to originate in the internal organs. For centuries the term nervous meant “neurological”, pertaining more to the body than mind. Nervous disorders included epilepsy, contractions, paralysis, tremors, cramps, alcoholism, loss of sensations, tetanus, and gout.
In the early 1800s, many illnesses were still being called hysterical, even when there was nothing wrong with the uterus. When women had tremors, palpitations, or seizures, but the internal organs were not affected, they were called “nervous.”
A colleague of Thomas Edison, and budding New York City neurologist George Miller Beard, noticed this trend of increasing nervous disorders. In 1869, Beard published a paper in the New England Journal of Medicine, where he came up with the term neurasthenia, which means “weak nerves.” If there was nothing wrong with the organs, what was precipitating this “nervousness”?
The hormonal rollercoaster of light
Women are more sensitive to hormonal changes, which are directly influenced by fluctuations in the electromagnetic environment. For instance, more women tend to be afflicted with Lyme disease due to higher levels of the leptin hormone.1 When leptin increases as the result of a biotoxin exposure such as Lyme, there is a simultaneous decrease in melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). Our bodies produce MSH in response to the electromagnetic stimulus of ultraviolet light we get from the Sun. MSH then produces melanin, an anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic hormone. As the entire planet embraced electric lighting, more people began to work indoors.

In 1885, German physician Rudolf Arndt made a connection between neurasthenia and electricity. He did this at the height of industrialization, for which he was vehemently admonished by his fellows. Arndt proposed that “electro-sensitivity is characteristic of high-grade neurasthenia.”
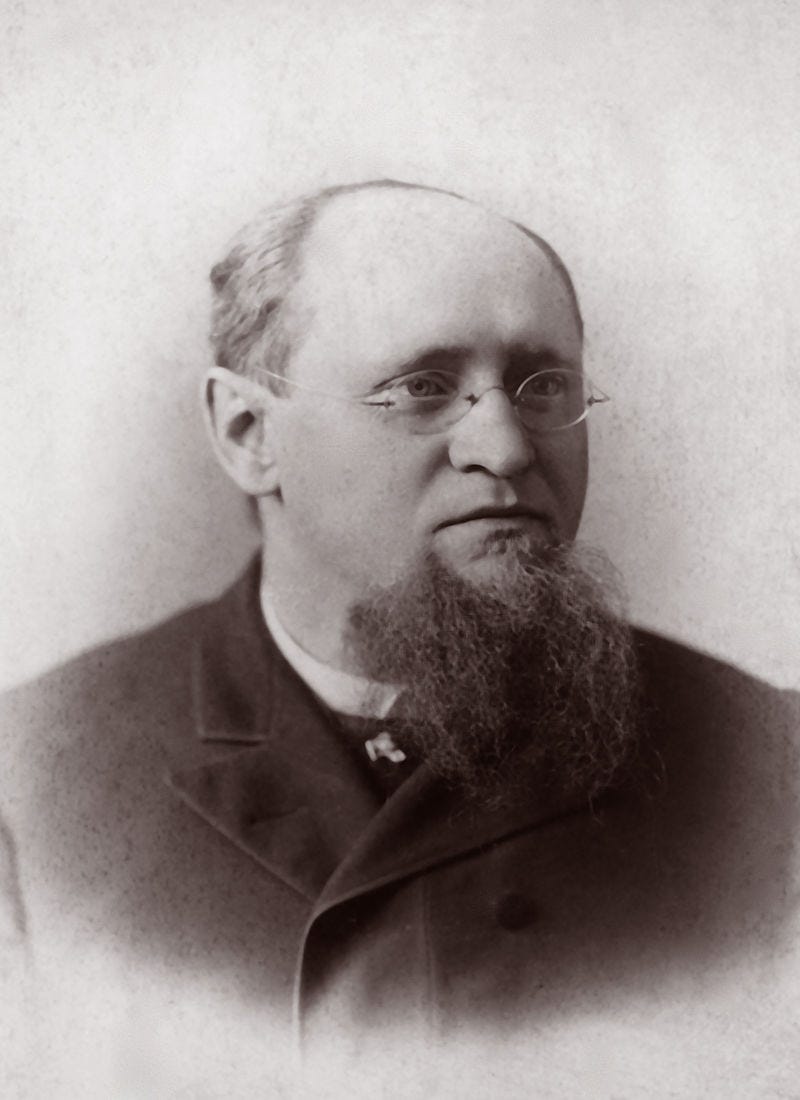

Arndt believed that a large obstacle to acknowledging electromagnetic poisoning was that the people who were less sensitive to electricity chalked up this study to the likes of superstition. Let us paint a picture of what was happening at that time, which was a systematic electrification of Earth.


New York & Stockholm: Today we don’t see many of those wires above - they’re conveniently wireless and out of sight, yet still run through our bodies.
The timeline leading up to the Dawn of Electricity:
1839 - Europe installs telegraphs
1844 - US installs first telegraph
1850 - telegraph lines are under construction on every continent. Twenty-two thousand miles of wire are energized in the US, four thousand through India, where “monkeys and swarms of large birds” are alighting on them.2
1875 - thirty thousand miles of submarine cable descends the depths of the ocean, and seven hundred thousand miles of copper web sprawls over the surface of the earth, enough to encircle the globe thirty times.
1885 - telegraph wires link almost thirty thousand homes and businesses over New York
1889 - Edison General Electric Co. is incorporated: every US city gets electric lighting, powered by AC (alternating current) motors. The Age of Electricity begins.
1897 - Marconi begins sending radio (wireless telegraphy) transmissions at one million cycles per second (our home wiring runs on 60 cycles per second)
Annual number of French studies on hysteria - peaks with the dawn of electricity Source:
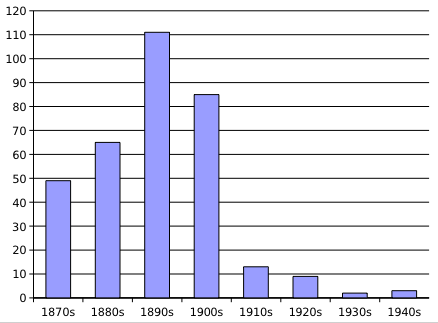
All of the great physicians of that time, and centuries before, ascribed to the fact that our bodies had their own DC (direct) electric current. Once disturbed, all our other biological functions would go astray. Industry had their way however, and did a better job of marketing their solutions that were seen as progress, over the seemingly backward philosophies of vitalists such as Newton and Galvani, who maintained there was an etheric vital force in each organism. In 1985, Robert Becker would go on to prove that this vital “life force” does in fact exist, in his book The Body Electric.
The most important observations made by the 19th century medical community regarding neurasthenia were that it:
-
Spread along routes of the railroads and telegraph lines
-
Affected both men and women, rich and poor
-
Also affected those who suffered from weather sensitivity
-
Sometimes resembled the common cold or flu
-
Ran in families
-
Increased likeliness of allergies and diabetes
-
Lowered tolerance for alcohol and drugs
-
Seized, most commonly, people in the prime of their life- 15 to 50yrs.
Then came the magic umbrella word to cover up industry’s pollution.
Over a century ago, at the dawn of an era that gave electricity its blessing to go full throttle not just for communication, but for light and power, Freud invented the term anxiety nervosa for these symptoms:
-
Irritability
-
Heart Palpitations, chest pain
-
Perspiration
-
Shortness of breath, asthma
-
Diarrhea
-
Vertigo
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Arthritis
-
Numbness and tingling
-
Tremor
-
Frequent urination
-
Insomnia
-
Ravenous hunger
-
Weakness
-
Exhaustion
All of the cases of neurasthenia, which were concerned with the nerves of the body, were now classified as a mental disease. Environmental illness caused by a toxic environment isn’t given as much credence to this day due to Freud, who blamed its symptoms on out-of-control emotions and disordered thoughts.
It is indeed “all in our head” when we allow the thought that “we’re bad” to be planted in our psyche.
Food for thought: some modern interpretations of Christianity tell us we’re all originally sinners. Are we? Or are we only souls seeking perfection? A sinner is a fixed label, whereas one who accepts their divine essence has room to grow.
How do you think the concept of a sinner may have an impact on our relationship with health and technology?
Because of Freud, environmental illness (illness caused by a toxic environment), is widely thought not to exist, its symptoms automatically blamed on disordered thoughts and out-of-control emotions.
“Because of Freud, we are today putting millions of people on Xanax, Prozac, and Zoloft instead of cleaning up their environment.”
~ Arthur Firstenberg, The Invisible Rainbow.
If all of this history seems out of the blue, I don’t blame you. It was the same for me, until I found I had been living under a rock called the U.S. In the International Classification of Diseases, code F 48.0 is for neurasthenia. This code was removed in the US version. Even in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-IV), the official system for assigning codes to mental diseases in American hospitals, there is no code for neurasthenia.
Most of the world still recognizes neurasthenia as one of the most frequently diagnosed diseases, usually indicating chronic toxicity. Physicians in these other countries take into consideration the effects of our environment and external stimuli, and have a holistic approach, vs our magic pills.
We hear it all the time: “mind is body.” What physically bridges the mind and body?
Our nerves.
If the bridge is out, how can we find a foothold in the stressed and tattered planks of our daily lives?
We can meditate, exercise, and eat well, however isn’t it easier to remove toxins at their core, rather than adding more to the equation?
In 2019, almost half of all US adults experienced some form of anxiety.3 In 2022, those suffering from anxiety incurred average annual medical costs of $11,711 to $18,045.4 Their total healthcare costs tended to be almost twice as high as those suffering without anxiety. The health and economic burden, including interference with performing daily activities, and an inability to function in society also contributed an average annual indirect cost of $7,500.
2022: Direct Healthcare-Related Costs Among Participants With GAD (generalized anxiety disorder):
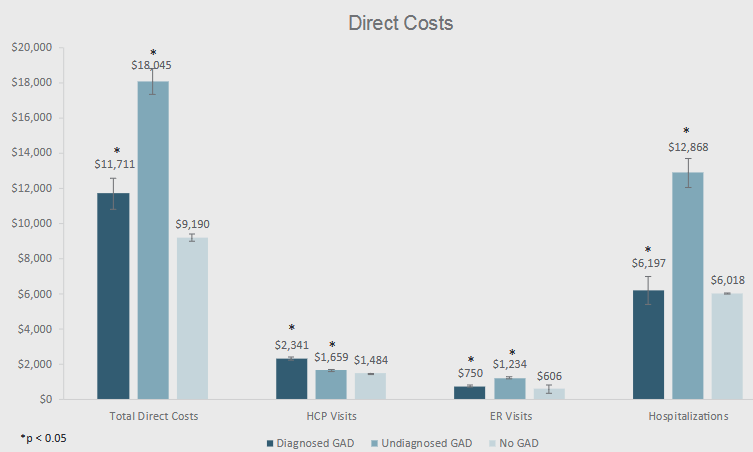
A 2025 study published in the journal PLOS Medicine found that young adults who experienced psychological stress as teens earned over $5,600 less in wages than those who didn’t.5 Finally, the researchers estimated that if a nationwide mental health expansion policy could reach just 10 percent of those stressed teens, the “labor supply impacts alone” would lead to an additional $52 billion in federal revenue over 10 years.
A 2024 analysis6 of commercial healthcare spending from Cedar Gate Technologies revealed the highest costs for behavioral and mental health are incurred by teens aged 15 to 19 years old with anxiety. This age group accounts for at least 31% more per-member per-month spending than any other. The study estimates that early intervention and effective treatment could save $3,321 per person in healthcare costs within two years.
Why don’t we remove the root of the anxiety, which is the nerve-wracking, neurologically-toxic wireless device that emits artificial light, instead of expanding more government programs? This would be a win-win for states who want to save money, and teens and adults who want to make more. The loser: Silicon Valley.
5 free ways we can lower anxiety
Indoor culture has accelerated and welcomed, with open arms and closed front doors, since the lockdowns of 2020. The lines between work, play, and family have been blurred. Many of us are at a loss, and accepted the cost, of being stranded on an island where screens seem to be the wave of a tireless future.
However, a bridge between that old way, and the new mind and body of today is being built, one nail at a time. Entrepreneurs are springing forth with new solutions to the anti-human technology of our past. We can create a new timeline for us all, as long as we have the vision, trust, and will to do it together. Many of our readers and colleagues are already forging the bricks of a more robust hereafter, providing solutions in their own lives like circadian armor, EMF shielding, blue light and dirty electrical filtration7, and daylight computers.
If you’re new here - welcome. We understand how overwhelming this can all be.
We used to feel the same way, until we found that taking one small step each day had a tremendous, positively palpable impact on our health.
Here are a few tactics you can try to reduce anxiety, which don’t cost us a thing, and that Bohdanna and I do daily in our lives:
The first two require almost zero effort (less-is-more):
-
Eliminate blue light at night - decreases levels of cortisol stress hormone, protects against low levels of melatonin.
-
Shut off Wi-Fi at night: wireless is invisible light, which keeps your brain alert and lowers melatonin - our growth hormone. A solid night’s rest is the best way to bring more calm into our lives.
The next three also cost nothing, just require a little effort that goes a long way:
-
Wim Hof breathing to regulate our nervous system - consistent practice leads to a stronger immune system, lower blood pressure, reduced levels of stress, and overall improved well-being.8
-
Cold showers/plunges - reduces cortisol, while cold water immersion at 14°C / 57° F has been shown to increase dopamine naturally by 250%.9
-
Sun exposure - increases MSH, which decreases stress response.
Which ones can you commit to right now?
Any tactics that have helped you reduce anxiety? We’d love to hear your feedback!
In a world gone mad, it’s okay to be a little crazy.
Just don’t go insane doing the same things, and repeating the same patterns day in and day out. New rhythms may be simple, but not always easy to introduce into our harried lives. That’s why we love getting out to see that Sunrise, rain, snow, or shine.
Instead of our hectic days going off with the blast of a starting gun, why not let them quietly unravel with the muffled calls of nature, and the cool, calm peace of a winter’s morning?

We are more powerful than we know,
Roman & Bohdanna
GET OUR MORNING POWER RHYTHM
Learn how to harness your LIFE FORCE, and activate the free medicine cabinet already within!

